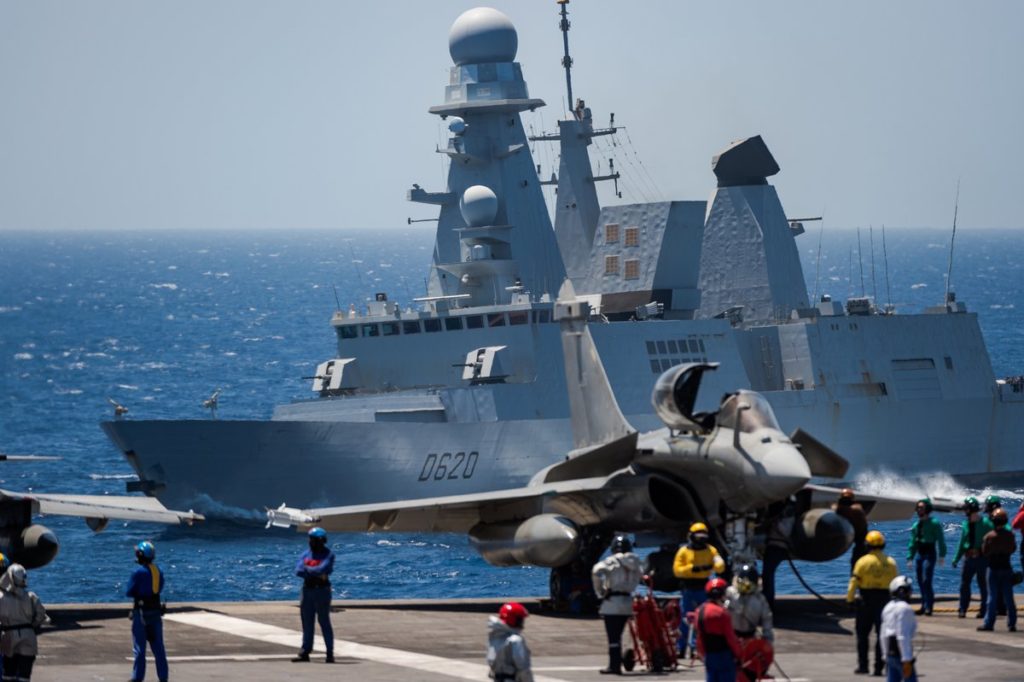
Horizon-class air defense destroyer Forbin remotely engaged a target (with an ASTER 30 surface to air missile) using a radar track shared via data-link by the FREMM frigate Languedoc.
The event, a milestone for the French Navy (a first in Europe, for a European navy), took place on September 18 2019 during the “Gabian” training exercise, a recurring exercise involving several vessels based in Toulon, on France’s Southern coast.
According to the French Navy, the success of this cooperative engagement validates the robustness of the data link architectures between its surface combatants and demonstrates their ability to share the tactical situation and coordinate their sensors and effectors in order to conduct air defense missions in combat situations.
These training exercises with live firings are essential for the operations of tomorrow and are therefore an essential preparation for a “Combatant Navy” which calls for units, weapon systems and crews to be experienced and therefore well trained.
From its DGA missile testing center on the Ile du Levant, the Directorate General of Armament (DGA) took part in this exercise, as in every training of this type, notably through the general coordination of the test and the implementation of the target materializing the threat. As more and more often for the operational readiness of the French forces, the virtual reality capabilities of DGA Missile Tests were also used. Thus, in order to enrich the tactical situation of the two vessels, the center transmitted data via link 16 creating a hybrid environment associating real tracks and simulated tracks. This capability provides the French Navy a training environment ever more representative of real warfare environment.
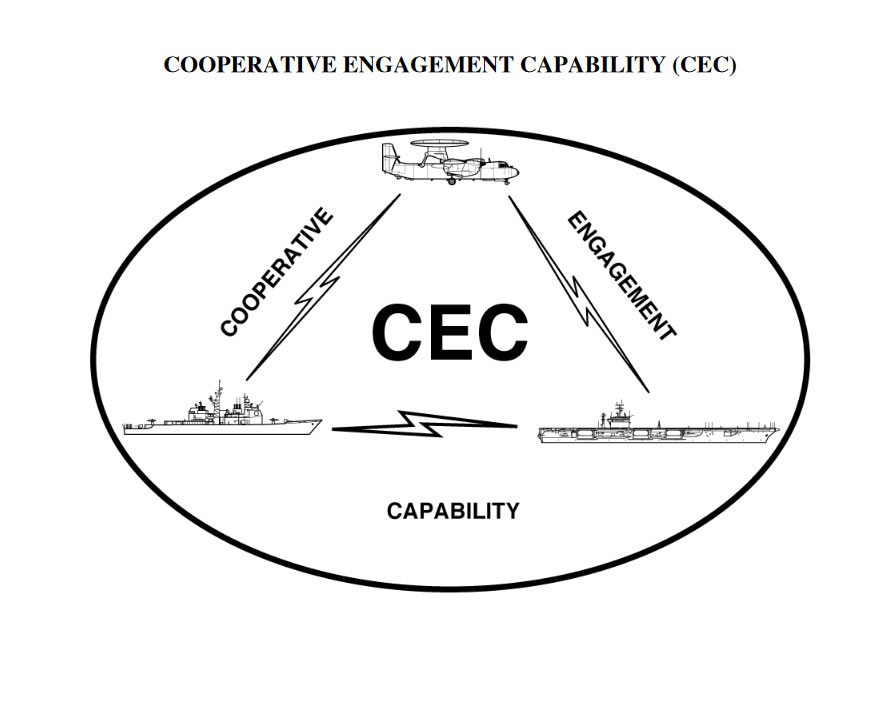
Veille Coopérative Navale: The French CEC
The “Veille Coopérative Navale” (naval cooperative watch) is a capability currently under development based on the principle of networking all the data of the sensors of a naval air force. It differs from tactical data linking by exchanging raw and much more accurate information directly from sensors, not from elaborate data. In the future, with the Veille Coopérative Navale , the French Navy will have an optimized picture of the threat and sufficient information to implement even more effectively an anti missile system, facilitating the choice of the most suitable platform to deal with the threat.
Veille Coopérative Navale relies among other things on V/UHF means made available by RIFAN step 2. The RIFAN (Réseau IP de la Force AeroNavale or naval and naval aviation’s IP network) was qualified in its “step 2” by the DGA in November 2015.
The U.S. Navy’s Cooperative Engagement Capability (CEC) is a real-time sensor netting system that enables high quality situational awareness and integrated fire control capability. It is designed to enhance the anti-air warfare (AAW) capability of surface vessels and aircraft by the netting of geographically dispersed sensors to provide a single integrated air picture, thus enabling Integrated Fire Control to destroy increasingly capable threats such as cruise missiles and aircraft.
The U.S. Navy is to date the only user of that technology with the Royal Australian Navy (aboard their AWD Hobart-class Destroyer) but Japan will soon follow, with the induction of their E-2D Advanced Hawkeye and their latest AEGIS destroyers.








